Thorough testing and validation of electrical panel assemblies are essential to maintain operational safety and performance. Effective procedures identify potential faults, confirm compliance with industry standards, and prevent failures during actual use. This article outlines key practices for testing and validating electrical panel assemblies before deployment, with a focus on precision and reliability in every step.
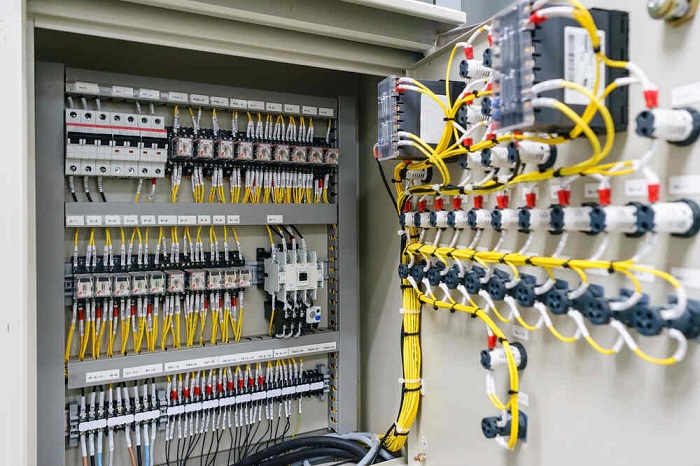
Best Practices for Testing and Validating Electrical Panel Assemblies Before Deployment
Visual Inspection and Documentation Review
The first step in testing montaje de cuadros eléctricos involves a comprehensive visual inspection. This process identifies physical defects, such as damaged components, loose connections, or improper wiring. Careful examination of all electrical connections, insulation, and labeling is necessary to prevent issues during operation.
A thorough review of design documentation is also required. Verifying that the assembly aligns with the provided schematic diagrams and technical specifications ensures consistency. Any discrepancies between the physical panel and the design documents must be corrected before proceeding to further tests.
Conducting Continuity and Insulation Resistance Tests
Continuity testing is critical for confirming that electrical paths are correctly connected without open circuits. This test involves checking each wire and connection point using a multimeter or continuity tester.
Insulation resistance tests assess the quality of insulation between conductors and ground. These tests use a megohmmeter to apply a high voltage, measuring resistance levels. Adequate insulation prevents current leakage, reducing the risk of electrical faults and equipment failure.
Verifying Electrical Functionality
Functional testing validates the operation of all electrical components within the panel. Each circuit, breaker, and relay must undergo testing under simulated load conditions to confirm proper performance. This step often involves activating control systems, measuring voltage and current, and verifying response times.
Testing under real-world conditions provides accurate performance data. If discrepancies arise, adjustments should be made to align the panel’s operation with specified parameters.
Thermal Imaging for Heat Detection
Thermal imaging identifies potential overheating and loose connections that may not be visible during visual inspections. By using infrared cameras, technicians can detect abnormal temperature variations in electrical panel assemblies. This non-invasive method helps locate hotspots that could indicate faulty wiring or overloaded circuits.
Regular thermal scans provide a baseline for future maintenance and early detection of developing issues, enhancing the panel’s long-term reliability.
Load Testing for Performance Assessment
Load testing evaluates the electrical panel’s ability to handle expected operational demands. This involves simulating the panel’s working environment and applying measured electrical loads to assess performance under stress.
During load tests, measurements of voltage drops, current flow, and temperature changes are recorded. Any deviations from expected values require further investigation to identify and resolve the cause.
Grounding and Bonding Verification
Proper grounding and bonding are essential for electrical safety. Testing the integrity of grounding connections ensures that electrical faults are safely directed to the ground, preventing hazards.
Ground resistance tests confirm that the panel meets required standards for safety and performance. Inaccurate grounding can lead to electrical shock risks and equipment malfunctions.
Conclusion
Adopting best practices for testing and validating electrical panel assemblies enhances their reliability before deployment. Regular testing, precise documentation, and adherence to standards are essential to maintaining quality and preventing operational failures.
Leave a comment